ML/AI
What is computer vision
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that essentially gives computers the ability to see and understand the world around them. Just like humans use their eyes and brain to take in visual information and make sense of it, computer vision uses cameras and algorithms to do the same thing.
Why Computer Vision?
The goal of computer vision is to replicate the complex and powerful capabilities of human vision by acquiring, processing, analyzing, and understanding images and, in general, high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information.
Computer vision leverages various techniques, including machine learning (ML), deep learning, and neural networks, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), to achieve these tasks with high accuracy and efficiency.
Applications of computer vision
Medical Imaging: Analyzing medical images to assist in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Autonomous Vehicles: Enabling self-driving cars to perceive and navigate their environment.
Surveillance: Monitoring and analyzing security footage.
Augmented Reality (AR): Integrating digital information with the user's environment in real time.
Facial Recognition: Identifying and verifying individuals from facial images.
Industrial Automation: Inspecting products and processes in manufacturing.
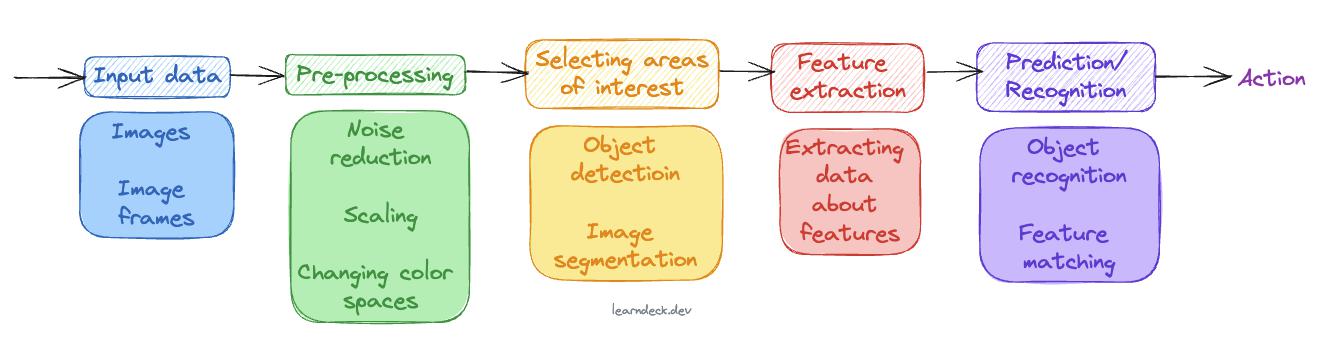
Computer Vision Pipeline
A computer vision pipeline consists of several stages, each focusing on a specific aspect of processing and analyzing visual data. The stages can vary depending on the specific application, but a typical computer vision pipeline includes the following steps: